
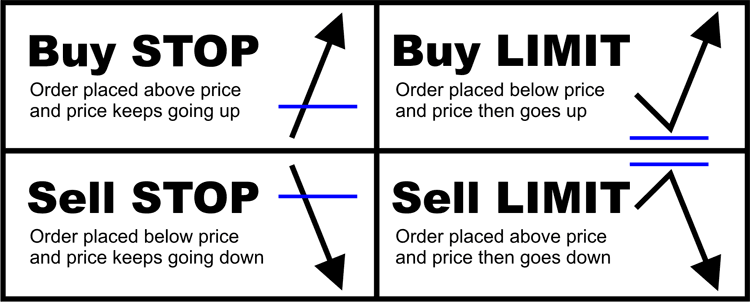
ET, during the weekend, or on holidays will be active the next trading day. ET, and is active for up to 180 calendar days (unless filled or canceled). Order is active for all equity trading sessions, from 7 a.m. Order is active during all equity trading sessions, from 7 a.m. ET, during the weekend or on holidays will be active the next trading day. ET, and active for up to 180 calendar days (unless filled or canceled). Order is active between the hours of 9:30 a.m. Order is active for one regular trading session only (or the remainder of the trading session if the order is entered while the market is already open). For example, a buy order could execute below your limit price, and a sell order could execute for more than your limit price.Īt Schwab, you have several options for how long your limit order stays active. (Limit orders are generally executed on a first come, first served basis.) That said, it's also possible your order could fill at an even better price. In that case, there may not be enough (or additional) sellers willing to sell at that limit price, so your order wouldn't be filled. Note, even if the stock reached the specified limit price, your order may not be filled, because there may be orders ahead of yours. If the stock failed to rise to $142 or above, no execution would occur.

If the stock rose to that level or higher, the limit order would be triggered and the order would be executed at $142 or above. A trader who wanted to sell the stock when it reached $142 would place a sell limit order with a limit price of $142 (red line).If the stock failed to fall to $133 or below, no execution would occur. If the stock fell to that level or lower, the limit order would be triggered and the order would be executed at $133 or below. A trader who wanted to buy the stock only if it dropped to $133 would place a buy limit order with a limit price of $133 (green line).A trader who wanted to purchase (or sell) the stock as quickly as possible would place a market order, which would in most cases be executed immediately at or near the stock's current price of $139 (white line)-provided that the market was open when the order was placed and barring unusual market conditions.In this example, the last trade price was roughly $139. The above chart illustrates the use of market orders versus limit orders. Between market sessions, numerous factors can impact a stock's price, such as the release of earnings, company news or economic data, or unexpected events that affect an entire industry, sector, or the market as a whole. A market order placed when markets are closed would be executed at the next market open, which could be significantly higher or lower from its prior close. Generally, market orders should be placed when the market is already open. Therefore, when placing a market order, the current bid and offer prices are generally of greater importance than the last trade price. This might also be the case in fast-moving markets, when stock prices can change significantly in a short period of time. However, the last trade price may not necessarily be current, particularly in the case of less-liquid stocks, whose last trade may have occurred minutes or hours ago. A market order is generally appropriate when you think a stock is priced right, when you are sure you want a fill on your order, or when you want an immediate execution.Ī few caveats: A stock's quote typically includes the highest bid potential buyers are willing to pay to acquire the stock, lowest offer potential sellers are willing to accept to sell the stock, and the last price at which the stock traded. Market orders are optimal when the primary goal is to execute the trade immediately. A market order typically ensures an execution, but it doesn't guarantee a specified price. Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) InvestingĪ market order is an order to buy or sell a stock at the market's current best available price.Bond Funds, Bond ETFs, and Preferred Securities.ADRs, Foreign Ordinaries & Canadian Stocks.Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) ETFs.Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Mutual Funds.
Benefits and Considerations of Mutual Funds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
